
- NAME: Michael Jackson
- OCCUPATION: Dancer, Songwriter, Music Producer, Singer
- BIRTH DATE: August 29, 1958
- DEATH DATE: June 25, 2009
- PLACE OF BIRTH: Gary, Indiana
Contents
Early Life
Michael Joseph Jackson was born on August 29, 1958, in Gary, Indiana, to an African-American working-class family. His father, Joseph Jackson, had been a guitarist but had put aside his musical aspirations to provide for his family as a crane operator. Believing his sons had talent, he molded them into a musical group in the early 1960s. At first, the Jackson Family performers consisted of Michael's older brothers Tito, Jermaine and Jackie. Michael joined his siblings when he was five, and emerged as the group's lead vocalist. He showed remarkable range and depth for such a young performer, impressing audiences with his ability to convey complex emotions. Older brother Marlon also became a member of the group, which evolved into the The Jackson 5.Behind the scenes, Joseph Jackson pushed his sons to succeed. He was also reportedly known to become violent with them. Michael and his brothers spent endless hours rehearsing and polishing up their act. At first, the Jackson 5 played local gigs and built a strong following. They recorded one single on their own, "Big Boy" with the b-side "You've Changed," but it failed to generate much interest.
The Jackson 5 moved on to working an opening act for such R&B artists as Gladys Knight and the Pips, James Brown, and Sam and Dave. Many of these performers were signed to the legendary Motown record label, and it has been reported that Gladys Knight may have been the one to tell Motown founder Berry Gordy about the Jackson 5. Impressed by the group, Gordy signed them to his label in 1968.
Relocating to Los Angeles, Michael and his brothers started work on their music and dancing with their father as their manager. They lived with Gordy and also with Supremes singer Diana Ross when they first arrived there. In August 1969, the Jackson 5 was introduced to the music industry at a special event, and later served as the opening act for the Supremes. Their first album, Diana Ross Presents the Jackson 5, hit the charts in December of that year. It's first single, "I Want You Back," hit No. 1 on the Billboard Hot 100 chart in January 1970. More chart-topping singles quickly followed, such as "ABC," "The Love You Save" and "I'll Be There."
Solo Career
At the age of 13, Jackson launched a solo career in addition to his work with the Jackson 5. He made the charts in 1971 with "Got to Be There" from the album of the same name. His 1972 album, Ben, featured the eponymous ballad about a rat. The song became Jackson's first solo No. 1 single.For several years, Michael Jackson and the Jackson 5 maintained a busy tour and recording schedule, under the supervision of Berry Gordy and his Motown staff. Gordy wrote many of the songs recorded by the group and by Michael Jackson as a solo artist. The group became so popular that they even had their own self-titled cartoon show, which ran from 1971 to 1973.
Despite Jackson's individual achievements and the group's great success, there was trouble between the Jacksons and their record company. Tensions mounted between Gordy and Joseph Jackson over the management of his children's careers,
and their level of participation in making their music. The Jacksons wanted more control over their recordings, which led to most of the Jacksons breaking ties with Motown in 1975. Jermaine Jackson remained with the label and continued to pursue a solo career, having previously released several albums—none of which had matched the success of his younger brother Michael.
Now calling themselves the Jacksons, the group signed a new recording deal with Epic Records. With 1978's Destiny, Michael Jackson and his brothers (which by now included younger brother Randy) emerged as talented songwriters, penning all of the record's tracks. Working with producer Quincy Jones, Michael Jackson wowed the music world with his next solo album, 1979's Off the Wall. It featured an infectious blend of pop and funk with such hit tracks as the Grammy Award-winning "Don't Stop 'til You Get Enough," "Rock with You," and the title track. He also found success with the ballad "She's Out of My Life."
The overwhelmingly positive response to Michael's latest solo album also helped buoy the Jacksons' career as well. Triumph (1980) sold more than one million copies, and the brothers went on an extensive tour to support the recording. Jackson, however, began to branch out on his own more. Teaming up with rock legend Paul McCartney, Jackson sang on their 1982 duet, "The Girl Is Mine," which nearly reached the top of the pop charts.
The song also appeared on his next solo album, Thriller (1982), which generated seven Top 10 hits and became the best-selling album in history. On a television special honoring Motown, Jackson performed "Billie Jean" -- eventually a No. 1 hit -- and debuted his soon-to-be-famous dance move called "The Moonwalk." Jackson, a veteran performer by this time, created this step himself and choreographed the dance sequences for the video of his other No. 1 hit, "Beat It."
His most elaborate video, however, was for the album's title track. John Landis directed the horror-tinged video, which featured complex dance scenes, special effects and a voice-over done by actor Vincent Price. The video for "Thriller" became immensely popular, boosting sales for the already successful album. It stayed on the charts for 80 weeks, holding the No. 1 spot for 37 weeks. In addition to its unparalleled commercial achievements, "Thriller" earned 12 Grammy Award nominations and won eight of those awards.
Jackson's Grammy victories showcased the diverse nature of his work. For his songwriting talents, he received the Grammy Award for Best Rhythm and Blues Song for "Billie Jean." Jackson also won Best Pop Vocal Performance, Male for "Thriller" and Best Rock Vocal Performance, Male for "Beat It." With co-producer Quincy Jones, he shared the Grammy Award for Album of the Year.







 04.27
04.27
 Jojo_deep
Jojo_deep







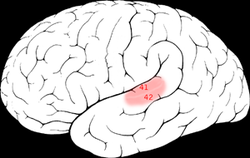




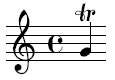

 Music is an
Music is an  Research has shown that music has a profound effect on your body and
psyche. In fact, there’s a growing field of health care known as
Research has shown that music has a profound effect on your body and
psyche. In fact, there’s a growing field of health care known as 
